Chapter 2 - Global E-Business and Collaboration
3/20 ~ 3/29
- 1: Business Processes and Information Systems
- 2: Types of Information Systems
- 3: Systems for Collaboration and Social Business
- 4: The Information Systems Function in Business
1: Business Processes and Information Systems
Business Processes
- introduced in Chapter 1 : manner in which work is organized, coordinated, and focused to produce a valuable product/service
How IT Improves Business Processes
- automation
- change flow if information
- more people to access + share info
- sequential steps replaced by simultaneous tasks
- elimate delays in decision making
frequently change the way business works, entirely new business model surfaces
ex: online downloading services by analyzing business processes \(\rightarrow\) achieve clear understanding of how business actually works
- conducting business process analysis \(\rightarrow\) understand how to change business to make it more efficient or effective
2: Types of Information Systems
Systems for Different Management Groups
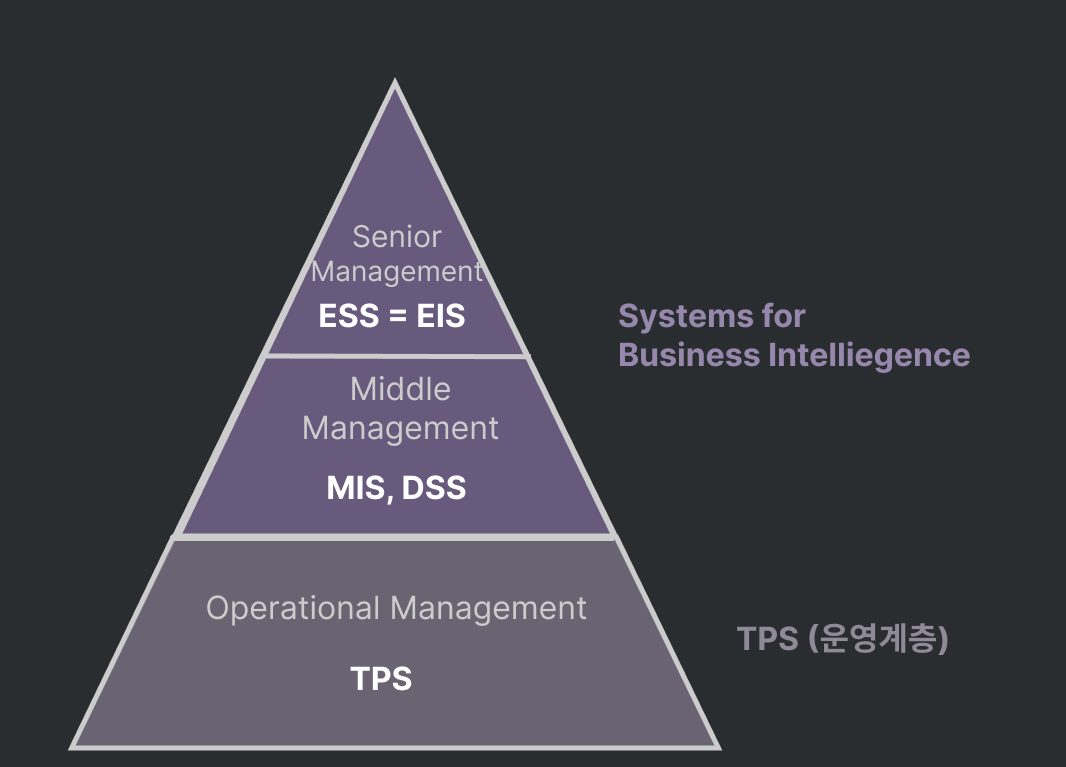
Transaction Processing Systems
TPS (거래 처리 시스템)
- 양, 횟수 多
- 거래 내역 관련 정보를 보관 및 관리
Systems for Business Intelligence
-
Management Information System (MIS): 작은 의미의 MIS (책의 내용이 아닌)
- \(\Rightarrow\) Managerial Report System (MRS): 경영보고 시스템
- TPS에서의 data를 체계적으로 보고 및 정리
- on a routined basis
-
Decision-suppport systems (DSS)= Business Intelligent System (BIS): 의사결정 지원 시스템
- relatively non-routinary
- focus on problems that are unique and rapidly changing
- 전문가형 (통계, 디자인, 수학, Big Data)
-
Executive Support Systems (ESS): 중역 정보/지원 시스템
- 포털성 (portal) : 종합적인 정보를 볼 수 있는 문
- CEO: 종합성 必, 다 알아야 함
- dashboard is also helpful
- EIS: requires experts for improvements from various fields
- 포털성 (portal) : 종합적인 정보를 볼 수 있는 문
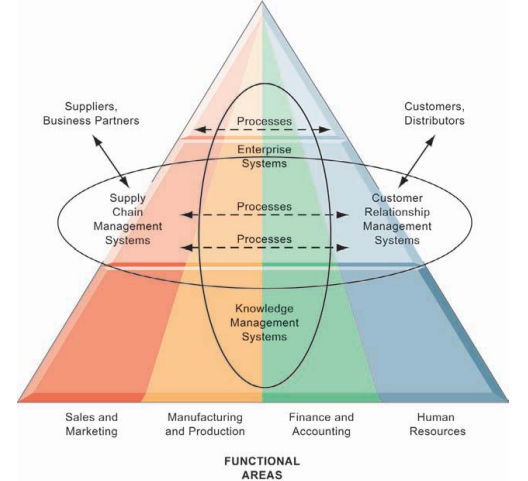
Systems for Linking the Enterprise
- Enterprise Applications
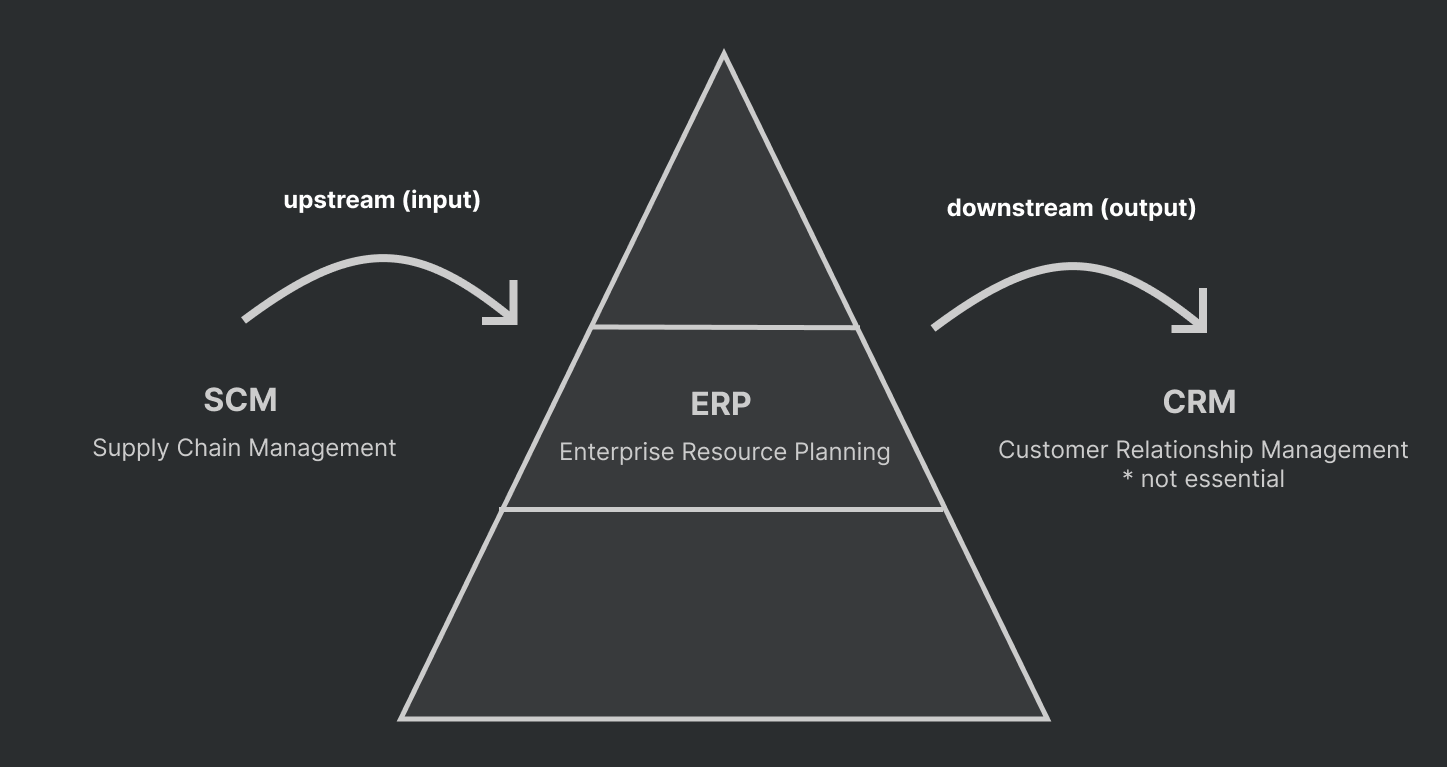
1. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning): aka Enterprise Systems
- : 전사적 관리 시스템
- integrate business processes to functions (일)
- information : fragmented in many different systems \(\Rightarrow\) sorted in single comprehensive data repository so that it can be used by any different parts of the business
- \(planning\) 은
계획이 아니라관리이다. - ERP의 유래:
- MRP (Material Requirement Planning) \(\rightarrow\) MRP II (Manufacturing Resource Planning) \(\rightarrow\) ERP (Enterprising Resource Planning)
- Module 식으로 되어 있음
- utlize Best Practice : 새로운 기능 도입 시 안 맞으면 우리의 ‘original’을 변형한다 (새로운 Best Practice는 유지) \(\Rightarrow\) ERP도입 시 과도한 Cutomization은 피한다
CEO의 의사결정이 중요! (
Bottom-up\(<\)Top-down)- ‘행정과 경영은 다르다’ (국가 = 행정, 회사 = 경영)
- ERP에서는 대장 (의사결정자)가 특히나 중요하다
- 하지만 도입 시 적절한 컨설팅과 교육과정 필요 (맨 땅에 헤딩 X)
- ex: 큰 돈 들여 import 했으나 rollback 가능성 있음
- 운영자의 역량에 따라 ERP도 달라짐 (like PPT..)
- 하지만 도입 시 적절한 컨설팅과 교육과정 필요 (맨 땅에 헤딩 X)
2. SCM (Supply Chain Management) Systems: 기존 유통관련 문제를 해결해준 시스템
- originally:
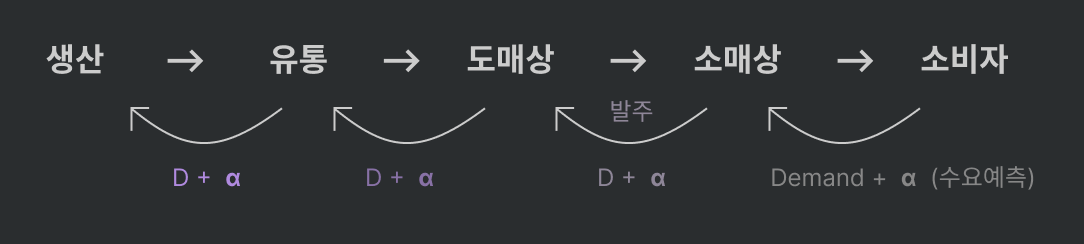
- α의 변화량: exponential; 다 어느정도 넉넉히 주문하기 때문
- 비효율적. (BUT 각 position은 최적의 의사결정을 함)
- \(\Rightarrow\)
Bullwhip Effect (채찍효과) (aka beer game)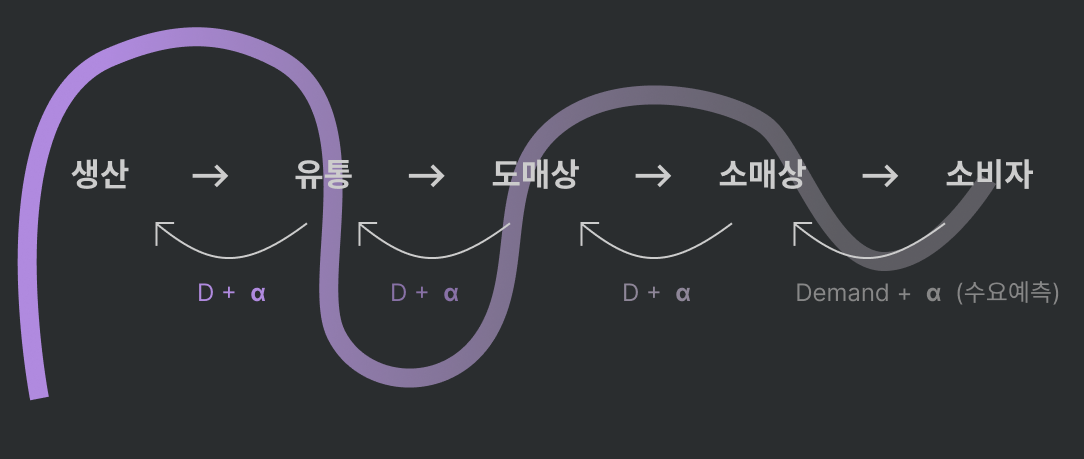
- α의 변화량: exponential; 다 어느정도 넉넉히 주문하기 때문
- NOW:

- 정보공유 필수 \(\Rightarrow\) 공급망의 효율성
3. CRM (Customer Relationship Management):
-
Contact Point : Customer DB \(\leftrightarrow\) 나 의 접점
- Call Center
- Inbound Call \(\curvearrowright\) CRM \(\curvearrowright\) Outbound
- 발신자 번호 (Caller ID) \(\longrightarrow\) DB
- (
CTI: Compute Telephony Integration)ex: 고객이 전화올 때 전화번호를 UserInfo로 변경해서 콜센터 직원에게 보여준다
- 영업사원 (Sales Center): frontier 인력, interacting with Customers
- Sales Force Automation (SFA): 정보기술의 도움으로 영업사원에게 대응능력을 길러준다 (≈정보화)
- ex:
흥정 시 계산, 납품관리, 등 의사결정 Empowerment - 의사결정은 최대한 빨리 현장에서 하는 것이 중요하다 - Empowerment: 권한 위임 및 RSC support - Delegate: 권한 위임
4. KMS (Knowledge Management Systems):
- more on Chapter 11…
Enterprise Application Architecture
E-Business, E-Commerce, and E-Government
- Digital Business
- E-Commerce: 다양하게 하게 사용되기 때문에 개념 정의 시 잘 알아야 할 것.
- Chapter 10
3: Systems for Collaboration and Social Business
Collaboration: 협업 (Teamwork)
-
Social Business - Social Enterprise (사회적 기업): 사회적 책임을 겸비하는 이윤을 창출하는 기업
- Social Technology (사회성 기술)
Applications of Social Business
Social Business Application Description 1 Social Networks connect through personal and business profiles 2 Crowdsourcing 일반 대중들 (crowd) 에게서 정보 수집 (not 내부직원/experts) 3 Shared Workspace co-create content (온라인 공간) like blackboard, google workspace 4 Blogs and wikis Publish and rapidly access knowledge; discuss 5 Social commerce purchasing (and opinions) through social platform 6 File sharing 7 Social Marketing SNS 홍보, interact / get insights from customers 8 Communities aka Forum, BBS (Bulletin Board System) - Collaboration and Social Business를 통한 기업의 성과 (종속변수) 중요
Tools and Technologies for Collaboration and Social Business
- Email and Instant Messaging (IM)
- 가장 기본적,
Teams,Discord,Slack - 교수님 추천: 이메일주소 4개는 가지고 있을 것
- 가장 기본적,
- Wikis (& Blogs)
- differs from wikipedia
- 홈페이지를 만드는 기술 (중 하나): 여러명이 동시접근, 동시편집 가능
- editable, therefore not 100% credible
- Collective Information: gradually goes towards the \(truth\)
- Virtual Worlds
- 2003 처음 용어 출시
universe: physically existingmetaverse: 1) Beyond 2) Explanation of something- 전처리 과정: check if input command is okay (not aggressive…etc)
- Collaboration and Social Business Platforms
videoconferencingsystemsZoom telepresence: remote but as if in present place
- ex: B2B회의 (교수님 의견, 모니터 그냥 큰거 하나만 둬도 됨…)
Time/Space Collaboration and Social Tool Matrix
- 그다지 의미 있는 표는 아님…
4: The Information Systems Function in Business
- specialists
- programmers
- System Analysts: translate business problems and requirements into information requirements and systems
- Information systems managers : leaders of teams
- C-levels
- CIO (Chief Information Officer): head of IS department
- CIO되면 딱히 올라갈 방법 없음 (Carreer is Over이라고도 한다고 함..)
- CSO (Chief Security Officer)
- CPO (Chief Privacy Officer)
- CKO (Chief Knowledge Officer)
- CIO (Chief Information Officer): head of IS department
End Users: 최종 사용자
- Review Questions
