Binary Classification
in Notes / Artificialintelligence / Introductiontoai
DAY 3
Binary Classification
Classify All Inputs into 0 or 1 (T / F)
Examples & Usages
- Spam Detection: Spam [1] or Ham [0]
- Facebook Feed: Show [1] or Hide [0]
- Credit Card Fraudulent Transaction Detetion: Fraud [1] or Legitimate [0]
- (determine transaction requested card is stolen or not)
- Tumor Image Detection in Radiology: Malignant [1] or Benigh [0]
- (determine whether certain cell is harmful or not)
threshold (한계점) - Ex) Quiz_grade >
50 ? PASS : FAIL - thresholds can change (if total = 1000, threshold = 50, if total = 10, threshold = 5)
- ➜ FIX THIS VALUE
- Ex) Quiz_grade >
Binary Classification Basic Idea
(Review) Deep Learning Steps
- Make Model
- Make Cost Function
- Optimize
Binary Classification Steps
- Step 1: Linear Regression with \(H(X) = WX + b\)
- Step 2: Logistic/sigmoid function \(sig(t)\) based on result of Step 1
TMI: it is called logistic in STATs, sigmoid in CS/EE area
| Linear Regression Model | \(+\) Sigmoid Function | ➜ Binary Classification Model |
|---|---|---|
| Wx + b | sigmoid (z) | sigmoid( Wx + b) |
| \(H(x) = Wx + b\) or \(H(X) = W^TX\) | \(g(z) = \frac {1}{1+e^{-z}}\) | \(g(X) = \frac {1}{1 + e^{-W^TX}}\) |
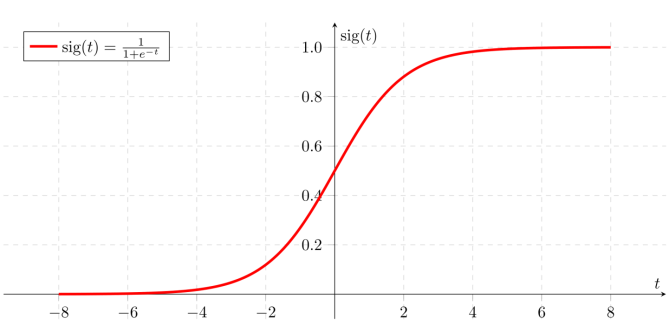
- any inputs (ranging from \(-\infty\) from \(+\infty\) can yield a \(y\) (result) value )
Linear Regression vs. BC
| Linear Regression Model | Binary Classification Model | |
|---|---|---|
| model | LINEAR | sigmoid(Wx + b) |
| cost | CONVEX ➜ GDM possible | \(avg( (model-y)^2 )\) ➜ GDM impossible |
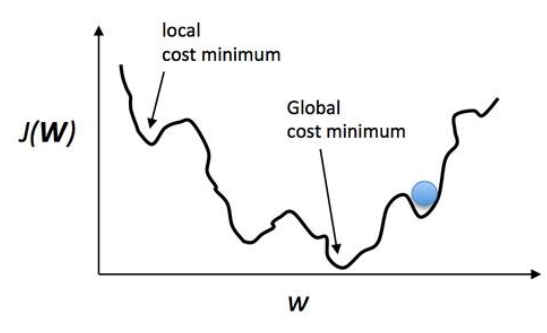
- if unlucky, global cost minimum cannot be achieved ➜
NEW COST FORMULA REQUIRED TMI: CONVEX = ∪ shaped
BC Cost Function
\[Cost(W) = \frac {1} {m} \sum \quad c(\quad H(x), \quad y\quad)\]written into: \[c(\quad H(x), y\quad) = \begin{cases} -log(\quad H(x)\quad) & y = 1 \\ -log(\quad 1 - H(x)\quad ) & y = 0 \end{cases}\]
- Understanding the Cost Function
| Cases: | A | B | C | D | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI model | \(H(X)\) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ex ) AI determines correct user is using the credit card |
| real data | \(y\) | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ex ) credit card is correctly used by ‘me’ (user) |
| \(Cost(W)\) | 0 | \(\infty\) | \(\infty\) | 0 |
ifAI is correct (CASE A, D) ➜ no CostelseCOST exists (either stealer uses my card (CASE B) or card suspened (CASE C))
log( 0 ) = \(-\infty\) ; log( 1 ) = 0
Further Explanations
- Case A: my card is not stolen and AI says its not stolen ➜ NO COST
- \(y = 0\) ➜ \(-log(1 - H(x))\) ⇒ -log ( 1 - 0 ) = -log( 1 ) = 0 (no cost)
- Case B: my card is stolen BUT AI says its not stolen ➜
COST : stealer uses my card- \(y = 1\) ➜ \(-log( H(x))\) ⇒ -log ( 0 ) = -log( 0 ) = \(-\infty\) (COST)
- Case C: my card is not stolen BUT AI says it’s stolen ➜
COST : I need to use but my card gets suspended- \(y = 0\) ➜ \(-log(1 - H(x))\) ⇒ -log ( 1 - 1 ) = -log( 0 ) = \(-\infty\) (COST)
- Case D: my card is stolen and AI says it’s stolen ➜ NO COST : Denies stealer’s transaction
- \(y = 1\) ➜ \(-log( H(x))\) ⇒ -log ( 1 ) = -log( 1 ) = 0 (no cost)
NEW COST FUNCTION (log-based) can derive CONVEX shape ➜ Gradient Descent Possible
ONE LINE EQUATION (since current Cost function is conditional)
- by multiplying \(y\) and \((1-y)\) on both equations and merging them, either one side gets elliminated
➜ Gradient Descent ( \(W \leftarrow W - \alpha \frac{\partial}{\partial W}\) ) Possible
PyTorch implementation🔥
import torch
import numpy as np
# Training Data (nonlinear)
x_train = torch.FloatTensor([[1,2], [2,3], [3,4], [4,4], [5,3], [6,2]])
y_train = torch.FloatTensor([[0], [0], [0], [1], [1], [1]]) # 0 or 1 (binary classification)
W = torch.randn([2,1], requires_grad=True)
b = torch.randn([1], requires_grad = True)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD([W, b], lr = 0.01)
def model_BinaryClassification(x):
return torch.sigmoid(torch.matmul(x, W) + b)
for step in range(2000):
prediction = model_BinaryClassification(x_train)
cost = torch.mean( (-1) * ((y_train*torch.log(prediction) + (1-y_train)*torch.log(1-prediction))))
#BC Cost Function: 1/m * -1 * y log H(x) (1 - y) log 1 - H(x)
optimizer.zero_grad() # 0까지 optimize
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
x_test = torch.FloatTensor([[5,5]]) #예상 답: 1 (PASS)가 나와야 함
model_test = model_BinaryClassification(x_test)
print("Model with [6,1] expectation: 1) in sigmoid: ", model_test.detach().item())
#0.5보다 높은지 안 높은지 실수형 (1.0, 0.0) 으로 변환
model_test_binary = np.round(model_test>0.5).type(torch.float32)
print("Model with [6,1] expectation: 1) in np.round: ", model_test_binary.detach().item())
