14 Big Data
in Notes / Dataanalytics / Datascience
What is Big Data
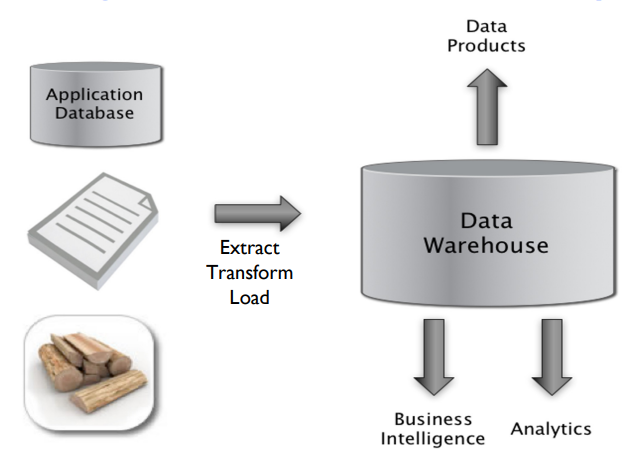
Big Data: Data of sizes beyond ability of traditional SW tools to quickly capture, curate, manage, and process
- unstructred (usually), semi-structured, structured data
- Data Lake: contains data inluding unstructured data
- unstructured data challenges:
- storing in DB not easy
- not easy to edit, search, analyze..etc
- unstructured data challenges:
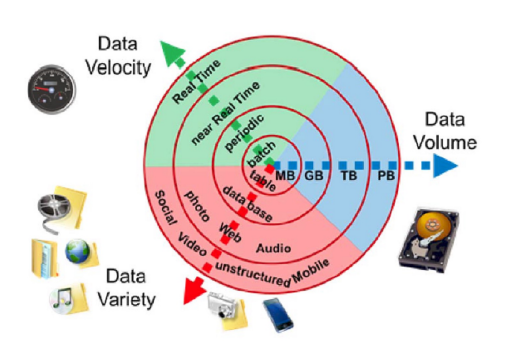
- The
3V : Velocity, Volume, Variety
Big Data come from:
- clicks, ad, server request, transanction…etc
-
Facebook's daily logs > 50 TB -
YouTube's DB cost > ad income - User Generated Content (Web & Mobile)
- Facebook, Instagram, Google…etc
- Health and Scientific Computing
- Graph Data (maps, social networks, telecom networks…)
- Log Files (Apache Web Server Log, Machine Syslog File)
- Aerospace : 25,000 sensors to optimize plane maintenance
- Autonomous Vehicles: 1.4-19TB / hr / car
- e-Commerce: using consumer data to enhance profit
Precision Medicine
- \(B \longrightarrow KB \longrightarrow MB \longrightarrow GB\) \(\longrightarrow TB \longrightarrow PB \longrightarrow EB \longrightarrow ZB \longrightarrow YB\)
- soon will reach 40EB/year by 2025
Data in Organization
-
Data Warehouse : collects and organizes data (from multiple sources)
- data periodically
ETL ‘d into data warehouse - Extracted, Transformed, Loaded
- data periodically
- Optimizing Data:
- reduce columns if not necessary
- partition tables
Dimension Tables: mutlidimensional ‘cube’ of data
Star Schema, Snowflake Schema
- Snowflake Schema: small size of tables all connected (might be quite challenging to analyze)
- OLAP: Online Analytics Processing (BI)
- user interacts with m-D data
using Tableau, Excel Pivot
- user interacts with m-D data
- Dealing with semi-structured or unstructred data
- enable data consumers to choose how to transform & use data
- PROBLEM: Dark Side of Data Lakes (DB become noisy, not 100% accurate (dirty data))
- \(\Rightarrow\) Data Analysts Required (데이터 규격화 必)
- Big Data Problems
- Data Structuring (데이터 규격화)
- Expensive Storage (CPU, hard drives)
Unstructured Datasets
- Requirements:
- Handle large files spanning multiple computers
- Use Cheap commodity devices that fail frequently
- Distributed data processing quickly and easily
- Solutions:
- Distributed File Systems
- Distributed Computing
Distributed File Systems
\(Q.\): Store and access very large files across cheap commodity devices 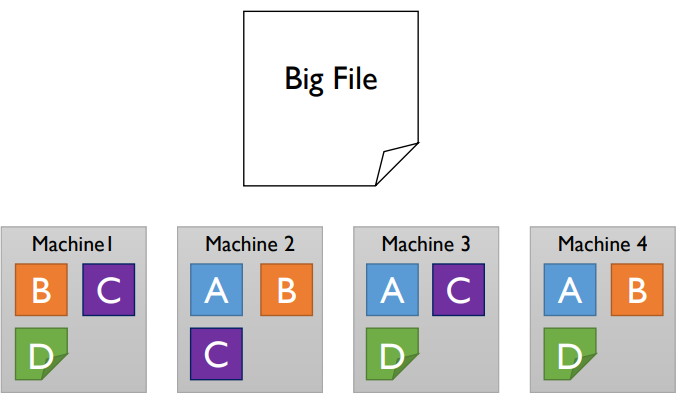
- split and make duplicates \(\rightarrow\) safer when machine fails since restorable
-
utilized by Google
-
Distributed Computing
Interacting with the data (Request / Response data samples)
-
Map-reduce distributed aggregation - Example Scenario:
- Computing number of occurences of each word in all the books using a team of people
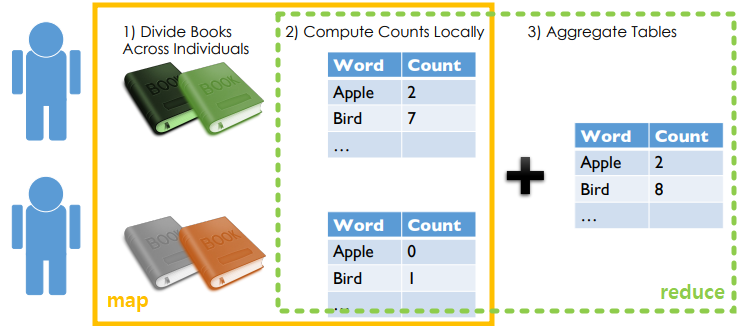
- divide and combine
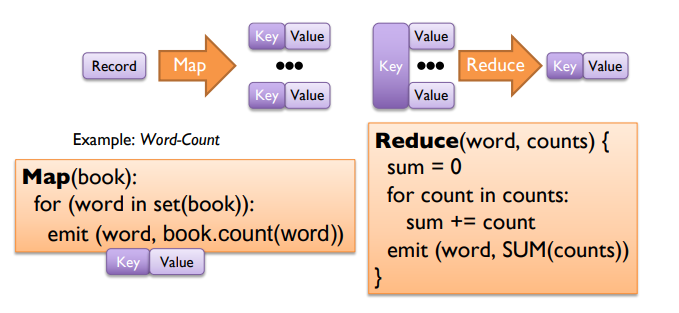
- used by Hadoop, Spark
